BrassRing’s new match score is designed to give another tool set to recruiters and hiring managers to ease overhead in reviewing high-value and highly attractive job postings.
Similarly, we leverage the same models to drive applicants to jobs that meet their skill set. Our first offering is a pair of feature sets described below, and it will be followed by like features that drive proactive sourcing for other open roles, campaign management, and many other tools.
Recruiter/Hiring Manager Match Score:
Available both from the dashboard as a sortable applicant field on the req and from other areas of the tool, like our two-way SMS dashboard, the Match Score field will show a comparison score for each applicant within a req based on their resume and the job itself.
The score is a combination of natural language processing to match skills and experience AI that compares the history of a candidate’s work experience for real-world skill applications and industry analysis to match skills that may be needed but not explicitly stated.
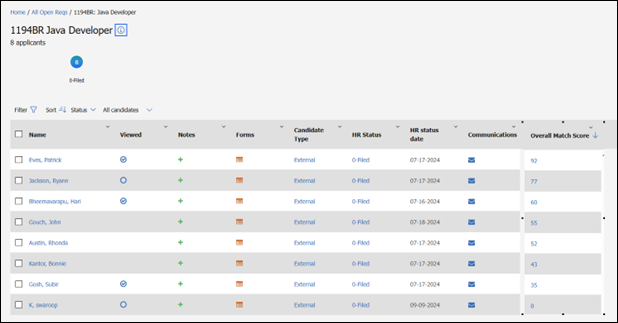
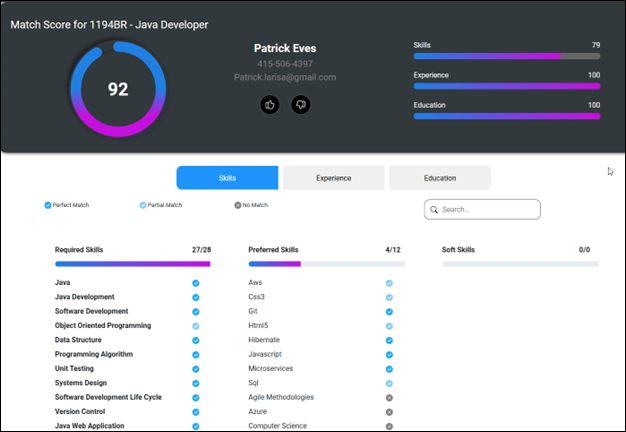
Once clicked, a new screen will show with skill details, as well as education and job experience tabs. Within the skills, items will show as full matches (dark blue), matches with less real-world experience (light blue), and non-matched skills.
This will soon be applied to a Speed Browse view and already comes RAM-ready so that actions can be taken to move those with the highest scores forward in the process while the rest of the candidates go through standard practice. This should provide immediate ROI for those massively attractive and hard-to-fill roles.
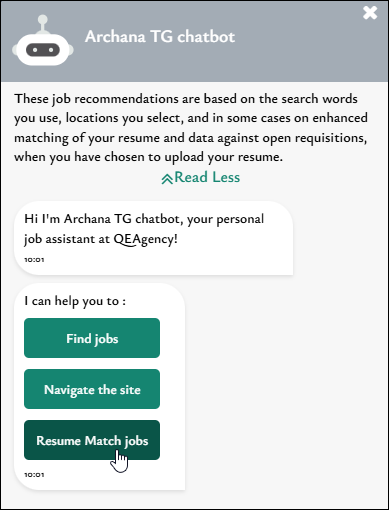
Applicant Job Search:
For the applicant, from Chat, Job search, and saved searches within Candidate Zone, clients can enable a resume match that produces similar results but with less specifics. Clients can set the threshold scoring to suggest jobs when a new or existing resume is uploaded.
We’ve leveraged our development history and skills in the AI HR space to focus on tools that will help applicants find jobs and teams find great resources for their companies. By partnering with Rchili for our data science, we can combine best-of-breed client experience with what adds value in this space with similar AI science to bring new opportunities to you.
What technology is used to score matches?
RChilli Search and Match Engine leverages, including semantic search, embeddings for job-role and skill matching, and hybrid search techniques that combine keyword-based and vector-based searches. These models evaluate text similarity, relevance, and context to ensure an accurate match between resumes and job descriptions.
The engine employs Natural Language Processing (NLP), Machine Learning (ML), and ontology-based techniques to analyze, categorize, and rank profiles. By breaking down unstructured data (resumes, job descriptions) into structured components (e.g., skills, experience, education), it ranks them based on relevance.
To calculate scores, RChilli uses a dynamic, configurable weight system that can be customized to client preferences. Scores are based on weighted factors available in the search document or query, and if entities are missing, scores are adjusted accordingly. A parent-child weightage system ensures accurate scoring by accounting for multiple entries matched to a single entity. The engine also leverages skill ranking and JobZone features to optimize score distribution across relevant criteria.
Reference:
https://docs.rchilli.com/kc/c_RChilli_search_match_Features_dynamic_weightage_searching
https://docs.rchilli.com/kc/c_RChilli_search_match_Features_job_zone_weightage
How non-direct matches are matched?
RChilli utilizes its proprietary taxonomy to enhance non-direct, or fuzzy, search capabilities. The taxonomy includes extensive datasets for job-related skills, job/skill ontologies, and other relevant information, allowing the engine to match profiles even when exact terms don’t align.
Related or similar terms: RChilli taxonomy recognizes variations in job titles and skills. For instance, a search for "software developer" might also match profiles with titles like "programmer" or "software engineer."
Skill proximity: Using job/skill ontologies, the engine identifies skills that are related or transferable, ensuring that candidates with similar qualifications are considered, even if exact terms aren't used.
Vector embeddings: RChilli also leverages vector embeddings to identify and match similar job profiles by analyzing contextual similarity and relevance.
By combining semantic search, synonym matching, taxonomies, and vector embeddings, RChilli expands the pool of potential candidates, ensuring that non-direct matches are effectively identified based on skill similarity, job title variations, and contextual relevance.
How is bias handled?
RChilli addresses bias by employing a transparent matching system that uses a well-defined, configurable weightage system. Clients can customize the weights or scores for specific entities according to their requirements. If certain entities should be ignored, they can be set to zero weight, meaning they will not contribute to the final match score.
RChilli's matching engine focuses primarily on job roles, skills, qualifications, and experience rather than attributes that could introduce bias. This ensures that the matching process is based on the most relevant job-related criteria.
To validate bias-free results, you can test two job descriptions with the same requirements but include biased entities (e.g., gender, age, race). When matched against the same set of resumes, RChilli’s system will return the same results, ensuring that non-relevant attributes have no impact on the matching outcome.
Reference:
https://docs.rchilli.com/kc/c_RChilli_search_match_Features_dynamic_weightage_searching
BrassRing Match Score Configuration Guide
Please refer to the BrassRing Match Score Configuration Guide Document to understand the best practices on the Match Score functionality.